What is PCOS? Polycystic ovarian syndrome, commonly referred to as PCOS, is the most widespread hormonal disorder affecting women. It impacts roughly 8-13% of women worldwide, equating to about one in ten, from the onset of menstruation until menopause. Women with PCOS often face irregular menstrual cycles, fertility challenges, acne, excessive hair growth, and weight gain.
PCOS is characterized by the formation of numerous small fluid-filled sacs around the ovary’s edge, medically known as cysts. These tiny cysts contain immature eggs, or follicles. In women with PCOS, these ovarian follicles don’t release eggs as they should, which can adversely affect overall reproductive health.
This article delves into PCOS, outlining its symptoms, risk factors, and causes. Keep reading to discover how to effectively manage this condition.
Understanding PCOS Symptoms
Hormones act as the body’s chemical messengers. In women with PCOS, there’s an overproduction of insulin and androgens (male-type hormones). Though the symptoms of PCOS can vary between women and may change over time, this hormonal imbalance can lead to several adverse signs and symptoms, including:
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
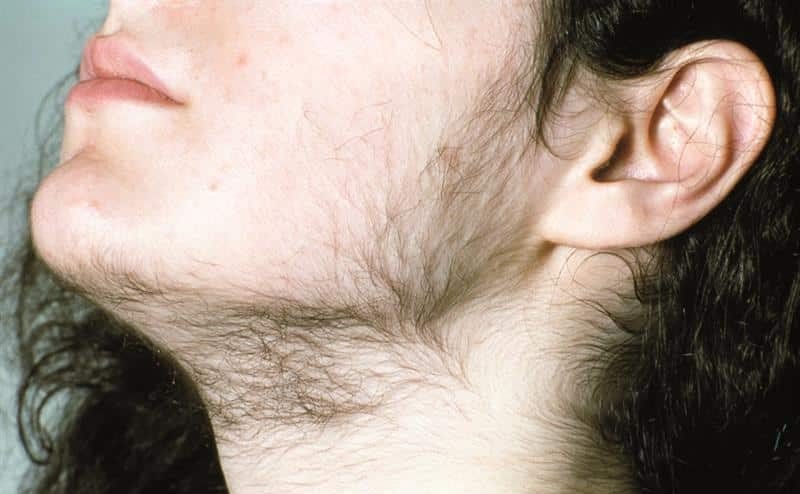
- Excessive hair growth on the face, stomach, and back
- Hair thinning or loss on the scalp
- Severe acne or pimples
- Weight gain
- Emotional distress, such as anxiety, depression, or poor body image
- Difficulty conceiving (infertility)
- Heightened risk of developing type 2 diabetes
Health Complications Related to PCOS
Weight Management. Many women with PCOS struggle with managing their weight, which can trigger an increased release of androgens.
Mental Health. Depression and anxiety are more frequently observed in women with PCOS, although the exact cause remains unclear. Experts believe it could be due to hormonal effects and the stress of dealing with PCOS symptoms.
Fertility Challenges. Due to hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual cycles, and weight issues, women with PCOS may find it challenging to conceive naturally. They might need to seek fertility support. As fertility rates decline after age 35, women with PCOS should consider family planning before this age to allow sufficient time for reproductive assistance if needed.
Other Health Concerns. PCOS is linked to a higher likelihood of developing several conditions, including prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, abnormal cholesterol and blood fat levels, and cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke. However, maintaining an active lifestyle, eating a healthy diet, and losing weight can significantly reduce these risks.
Causes of PCOS
PCOS can arise due to a combination of genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle factors. Women with a family history of PCOS in their mother, aunt, or sister are 50% more likely to develop the condition themselves. Some studies also suggest that PCOS is more prevalent among women of Asian, Aboriginal, Torres Strait Islander, and African descent.
While the precise cause of PCOS remains unknown, early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and weight management can mitigate the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.