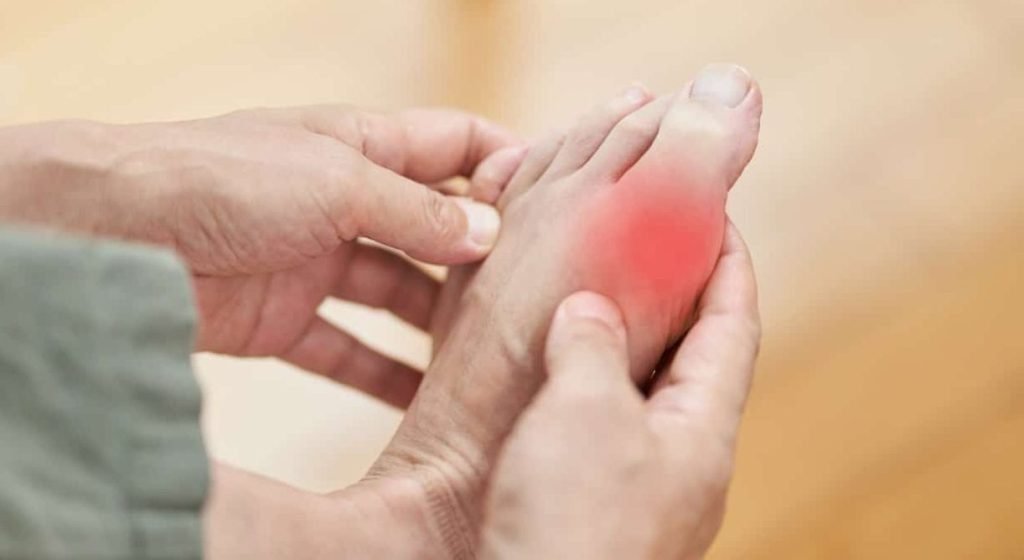
Hyperuricemia occurs when the [blood has a high level](https://prohealthsupporter.com/product-attribute/treats/high-blood-pressure/) of uric acid. Elevated uric acid levels can lead to various complications, including gout and painful arthritis. High uric acid levels are also associated with other health concerns such as cardiovascular disease, kidney illness, and diabetes.
Recent research indicates that 43.3 million Americans suffer from hyperuricemia and gout, marking the highest prevalence in the U.S. since the 1960 spike.
Although hyperuricemia itself is not a disease, prolonged elevated uric acid levels can lead to several adverse health conditions.
## **What Causes Hyperuricemia?**
Uric acid is produced when your body breaks down purines, which are found in foods like red meat, organ meat, seafood, and beans.
Hyperuricemia occurs either when your body produces too much uric acid or fails to excrete enough. Commonly, this condition arises when the kidneys cannot efficiently eliminate uric acid.
The excess uric acid in your body crystallizes and forms compounds, primarily around joints and the kidneys. Your immune system perceives these crystals as foreign materials, causing your white blood cells to attack them, resulting in pain and inflammation.
### Understanding Hyperuricemia Symptoms and Causes
[Hyperuricemia symptoms](https://prohealthsupporter.com/bystolic-alternatives/) manifest when there’s an excessive buildup of uric acid in the blood. Symptoms often include joint pain, swelling, and tenderness, particularly in areas like the big toe, ankles, knees, and wrists. Individuals might also experience severe discomfort during movement or even while at rest. The condition arises from factors such as the body producing too much uric acid, or the kidneys’ inability to filter it out adequately, along with lifestyle factors like a purine-rich diet. Identifying these symptoms and causes is essential for the timely diagnosis and effective management of hyperuricemia to prevent conditions like gout and kidney stones.
## **How to Treat Hyperuricemia?**
[Effective hyperuricemia treatment](https://prohealthsupporter.com/product-attribute/treats/hyperuricemia/) relies on determining its cause. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia often doesn’t require specific treatment. However, if hyperuricemia is linked to conditions such as gout, kidney disease, or certain medications, addressing these root causes is essential. Managing the underlying condition is crucial to reducing uric acid levels and preventing further complications. Treatment plans aim to alleviate symptoms and avoid recurring elevated uric acid levels, thus enhancing overall health and quality of life.
### Gout
To treat gout, one or more of the following medications may be used:
– Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
– Probenecid
– Allopurinol (Zyloprim) and febuxostat ([Uloric](https://prohealthsupporter.com/shop/uloric-80mg/))
– [Colchicine](https://prohealthsupporter.com/shop/colchicine-0-6mg/) (Colcrys)
### Kidney Stones
For kidney stones up to 5 millimeters in size, doctors may recommend drinking plenty of water and taking over-the-counter pain relievers until the stone passes. For kidney stones larger than 5 millimeters, prescription medications like Tamsulosin (Flomax) might be necessary.
In more complex cases where kidney stones exceed 10 millimeters, a surgical procedure called ureteroscopy may be required to remove the stones.
### **Dietary Changes**
A hyperuricemia-friendly diet can help control uric acid levels and prevent complications. It can reduce the risk of gout, kidney stones, and joint damage.
#### Foods to Avoid on a Hyperuricemia-Friendly Diet:
– Red meat
– High-glucose foods and beverages
– Organ meat (liver)
– Seafood (anchovies, sardines, scallops, and mussels)
– Spinach, mushrooms, and peas
– Beans
– Oatmeal
– Alcoholic beverages
– Yeast supplements
Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet and lifestyle is vital for managing uric acid levels in the blood. Following prescribed medications is essential to prevent the development of more severe chronic illnesses.